Read XML
This activity retrieves values from an XML document. There are a variety of ways to define the XML document.
![]() How does this activity look in the Designer Pane?
How does this activity look in the Designer Pane?
- Drag it from the Toolbox Pane and drop it in the Designer Pane.
To configure this activity
Select the activity in the Designer Pane to configure the following property boxes in the Properties Pane.
See the following options:
-
 Activity Name
Activity Name
Once added to a workflow definition, the default name of an activity can be changed. Providing a custom name for an activity helps you remember the role it plays.
To name an activity
- Add an activity to your workflow by dragging it from the Toolbox Pane and dropping it in the Designer Pane.
- Select the activity in the Designer Pane.
- Under Activity Name in the Properties Pane, replace the default name.
Note: Activity names cannot be the same as any other activity name in the workflow, they cannot be the same as the workflow's name, they must be less than 100 characters, they must contain at least one alphanumeric character, they cannot be "Name," and they cannot be the same as the activity's runtime type (which is usually only an issue with custom activities).
-
 Activity Description
Activity Description
Use the Activity Description to provide descriptive text to help you remember the role that the activity plays in the workflow. All activities contain a default description that you can modify while constructing your workflow.
To modify an activity description
- Add an activity to your workflow by dragging it from the Toolbox Pane and dropping it in the Designer Pane.
- Select the activity in the Designer Pane.
- Under
 Activity Description in the Properties Pane, replace the default description.
Activity Description in the Properties Pane, replace the default description.
-
 XML Source
XML Source
Use this property box to specify the XML document you want to process.
- Add the Read XML activity to your workflow definition by dragging it from the Toolbox Pane and dropping it in the Designer Pane.
- In the XML Source property box, specify the XML document you want to process. If the XML document is retrieved as part of a previous activity in the workflow, specify the desired token.
-
 XPath Expression Tokens
XPath Expression Tokens
Use this property box to configure the activity. Specify the XML document you want to traverse and an XPath expression for how to traverse the XML document.
To configure XML information
- Add the Read XML activity to your workflow definition by dragging it from the Toolbox Pane and dropping it in the Designer Pane.
- In the Properties property box, click New Token.
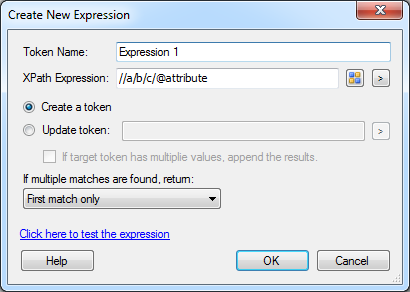
- Specify a token name.
- In XPath Expression, manually specify an appropriate XPath expression to traverse the XML document and select values or click
 to help you build an XPath expression.
to help you build an XPath expression. - Choose one of the following options:
- Create a token: Choose between choosing to create a new token
- Update token: or to store the result in an existing token.
- In the If multiple matches are found drop-down option, choose what happens when the specified XPath expression matches multiple nodes in the XML document.
Note: Click the Click here to test the pattern link, to display the Test Input text box. Paste or type a sample XML document to see the result of your XPath expression.
-
 Advanced Properties
Advanced Properties
Click the Advanced button
 at the top of the Properties Pane to:
at the top of the Properties Pane to:- Automatically remove default namespace declarations
- Define prefix-namespace mappings that will be in the XML source document
Clearing out default namespaces or defining the prefixed namespaces that will be available in the XML source document allow you to more easily construct XPath expressions without having to use wildcards to match any namespaces.
Example: A XML source document contains this namespace declaration: <xmlns:LF="http://laserfiche.com/namespaces/importengine">. After defining this LF prefix http://laserfiche.com/namespaces/importengine namespace pairing in a Read XML activity's advanced options, you can write an XPath Expression that uses the LF prefix like so: //LF:ElementName//@AttributeName.
- Click the area under XML Namespaces to display the XML Namespace Options dialog box.
- In the left column, specify the prefix associated with the namespace. In the right column specify the namespace associated with the prefix.
Tip: Use the Autodetect namespaces link to specify a sample XML document that has the desired namespace declarations to automatically define the available mappings.
- Select the Automatically clear default namespaces option to also clear out default namespace declarations in the XML source document.
Example: The response from an HTTP Web Request activity is an XML document that contains an element or attribute with a Laserfiche document ID. A Read XML activity can retrieve this document ID for use in a later step in the workflow.
Important: The Read XML activity supports XPath 1.0.